What is the architecture of AWS Control Tower and how are accounts organized within it?
AWS Control Tower is a service that simplifies the creation of a secure multi-account environment in AWS. Offering a high-level blueprint for setting up new AWS accounts enables seamless integration and management of existing resources. AWS Control Tower facilitates this process using AWS Organizations, AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM), and AWS Resource Linking, collectively enhancing resource accessibility and security across accounts.
Following the initial setup process, users make critical decisions about security and compliance settings, ensuring efficient management and access across accounts. AWS Control Tower’s automated processes reduce the need for manual intervention, thereby minimizing setup errors and enhancing security. Through testing and finalizing the setup, users can verify resource accessibility, confirm security compliance, and ensure that all business processes function correctly within the new Control Tower account.
It manages monitoring through a specific log archive account that centralizes all logs. It utilizes AWS CloudTrail to capture the activities within AWS Control Tower. Moreover, by leveraging CloudWatch Logs and CloudWatch Logs Insights, users can easily visualize and query the lifecycle events of AWS Control Tower. Each lifecycle event is documented only after particular actions have been executed, and details on the success or failure of the originating Control Tower action are provided. These events are automatically recorded as non-API AWS service events by AWS CloudTrail and are transmitted to Amazon EventBridge for further processing.
A Landing Zone is a configured structure that offers a compliant and secure set of accounts upon which to begin building. This Landing Zone can include additional features such as federated account access through Single Sign-On (SSO) and the utilization of centralized logging via Amazon CloudTrail and AWS Config.
Guardrails are rules written in plain English and implemented using AWS CloudFormation within the Landing Zone to enforce security requirements and maintain compliance. They ensure that each account within the Landing Zone adheres to specific security settings and configurations that meet the organization’s standards. Guardrails can either be mandatory, optional with flexibility to be toggled to meet specific requirements, or elective and aren’t on by default.
The organization of accounts within the Landing Zone is achieved through the use of Organizational Units (OUs), which are provisioned with the help of AWS Organizations. Let’s explore the OUs commonly utilized in the architecture of AWS Control Tower:
1. Security OU: This OU contains key accounts, such as the Log Archive Account and the Audit Account. It serves as a centralized store for CloudTrail and AWS Config logs, ensuring security and traceability across the entire infrastructure.
2. Sandbox OU: The Sandbox OU provides a safe and isolated environment for testing purposes. It houses Sandbox Accounts, which are used to conduct experiments and trials without risking disrupting production workloads.
3. Production OU: The Production OU houses all production accounts and their respective workloads. It is the main hosting environment for critical applications and services.
4. Non-Production OU: The Non-Production OU is dedicated to pre-production activities, enabling comprehensive application testing and development before being moved into the production environment.
5. Suspended OU: Accounts within the Suspended OU are securely isolated and have highly restricted permissions. This OU is designed to handle deleted, reused, or breached accounts, ensuring that any potential security risks are contained in a controlled environment.
6. Shared Services OU: The Shared Services OU contains accounts dedicated to services shared across multiple other accounts. This includes accounts for shared services, security services, and networking, which provide centralized services that can be leveraged by various accounts within the landing zone.
The architectural setup of AWS Control Tower, with the Landing Zone and its associated OUs, establishes a secure and organized environment for managing multiple accounts within the AWS ecosystem.
Features
AWS Control Tower maximizes visibility through the dashboard. All the provisioned environments, the number of guardrails enabled, and the status of all resources present are completely visible from this single UI. Review tools ensure that everything is compliant and what actions should be taken in the case of a lack of compliance.
Landing Zone
A landing zone is a multi-account AWS environment that has passed well-architected standards and meets the necessary compliance and security requirements. It is easy to automate new landing zone setup using blueprints with various preset features, including identity access management in conjunction with AWS IAM (link), federated access, centralized logging in conjunction with AWS CloudTrail, and security audits.
Account Factory
Account Factory is an automated solution that simplifies the process of procuring new accounts for your organization. It offers pre-configured and pre-approved templates that can be easily modified to align with your specific business and security policies. By leveraging these templates, you can ensure that the provisioning of new accounts adheres to the necessary standards and requirements.
With Account Factory, creating new accounts is streamlined and efficient. It eliminates the need for manual intervention, allowing builders to automate the setup of landing zones and provisioning of accounts. This automation saves time and reduces the chances of errors or inconsistencies.
The pre-configured templates provided by Account Factory cover various aspects, such as networking information and region selection. This ensures new accounts are provisioned with the necessary network configurations and deployed in the desired regions. By incorporating these pre-approved configurations, you can ensure a standardized and secure account provisioning process.
In addition to the pre-configured templates, Account Factory seamlessly integrates with AWS Service Catalog. This integration enables internal customers to easily configure and build new accounts, empowering them with self-service capabilities. By utilizing AWS Service Catalog, users can customize their accounts based on their specific requirements without relying on IT support or lengthy approval processes.
Account Factory also offers compatibility with third-party Infrastructure as Code tools like Terraform. This integration allows cloud teams to leverage familiar tools and workflows while still benefiting from the Account Factory’s capabilities. With the ability to use Terraform, teams can efficiently manage and deploy resources across multiple accounts, ensuring a seamless experience.
Controls
Mapping controls with AWS Control Tower isn’t as excessively complicated and will not take as much time to map, define, and manage which accounts have access or what data gets encrypted. AWS CloudFormation Hooks are now being used to identify and block resources that are not compliant with user-defined requirements regardless of the operation size and scale. Finally, configuration and technical documentation is kept updated so users remain informed.
Guardrails
As mentioned above in the segment about Landing Zones, guardrails are governance rules for either security or compliance that can be applied either across the enterprise or to specific accounts. Guardrails come in two different dimensions: preventive/detective and mandatory/optional.
-
- Preventive/detective: In the automated landing zone created by AWS Control Tower, guardrails play a crucial role in ensuring compliance and security. The guardrails are designed to establish intent and prevent the deployment of non-compliant resources while also detecting any existing noncompliant resources. By utilizing the preventive and detective aspects of guardrails, AWS Control Tower continuously monitors and updates the status on the dashboard to maintain a secure environment.
-
- Mandatory/optional: The governance provided by the guardrails is based on AWS best practices and common customer policies. Mandatory guardrails enforce strict controls, disallowing changes to IAM roles and bucket policies, detecting unauthorized access, and preventing certain cross-region activities. On the other hand, optional guardrails offer flexibility by allowing users to enable or disable them as needed. These guardrails help in detecting access to Amazon S3 buckets, ensuring MFA for root users is enabled, and confirming encryption for Amazon EBS volumes attached to EC2 instances.
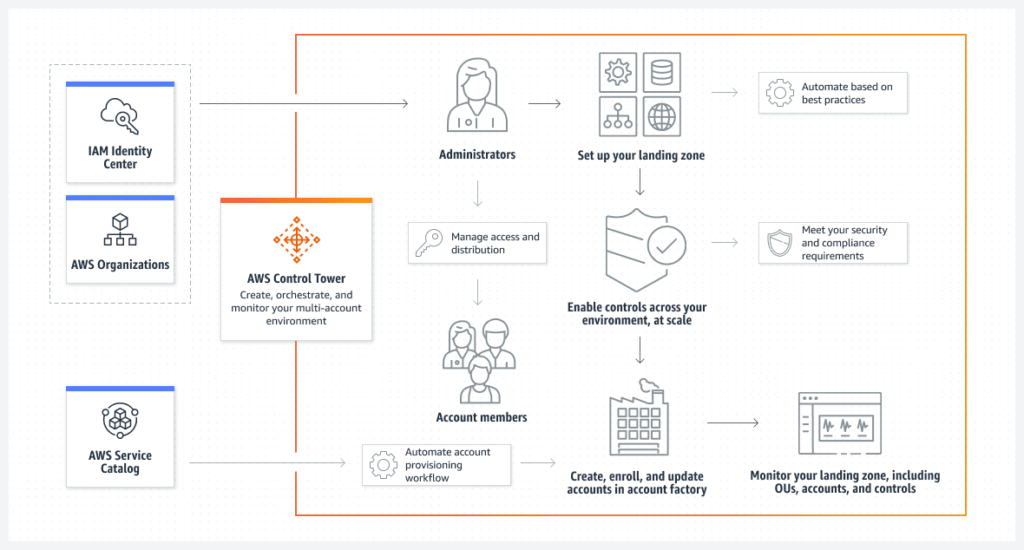
How to Start With AWS Control Tower
Here is a high-level plan for setting up AWS Control Tower on a new account and integrating existing AWS account resources with it:
- Preparation:
-
- Ensure you have the necessary permissions in both the new and existing AWS accounts to set up the Control Tower and integrate resources.
- Make a list of the resources in the existing account that you want to integrate with the new Control Tower account.
-
- Setting up AWS Control Tower:
-
- Create a new AWS account if you do not already have one.
- Set up AWS Control Tower in the new account.
- Follow the setup process and decide on the security and compliance settings you want to implement.
-
- Integrating existing resources:
-
- Use AWS Organizations to create an organization that includes both the new Control Tower and existing accounts.
- Ensure AWS resource access is set up correctly between the accounts using AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM).
- Utilize AWS Resource Linking to link the desired resources in the existing account to the new Control Tower account.
-
- Testing:
-
- Validate that the resources are accessible in the new Control Tower account.
- Verify that the security and compliance policies set up in Control Tower are being applied to the integrated resources.
- Ensure that all business processes are working as expected in the new Control Tower account.
-
- Finalizing:
-
- Document the process, including any changes made to the resources during the integration process.
- Train any necessary staff on the new processes and policies set up in the new Control Tower account.
-
To access AWS resources from one account to another, you can use AWS Organizations or AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM).
- Using AWS Organizations:
-
- Create an AWS Organization that includes both accounts.
- Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies to control access to resources across accounts.
- You can delegate access to the other account by granting permissions in IAM policies.
-
- Using AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM):
-
- Create a resource share in the account that owns the resources.
- Authorize other accounts to access the shared resources.
- Use IAM policies to control access to the shared resources.
-
Works With Existing or New
This service is perfectly capable of managing governance across both existing and new platforms built on AWS. It will only charge users depending on how much it is used on whichever AWS resources. If these steps in any way sound intimidating, Amazon also has a lab to learn and demonstrate Control Tower’s functionality.
How to Start With AWS Control Tower
Here is a high-level plan for setting up AWS Control Tower on a new account and integrating existing AWS account resources with it:
- Preparation:
-
- Ensure you have the necessary permissions in both the new and existing AWS accounts to set up the Control Tower and integrate resources.
- Make a list of the resources in the existing account that you want to integrate with the new Control Tower account.
-
- Setting up AWS Control Tower:
-
- Create a new AWS account if you do not already have one.
- Set up AWS Control Tower in the new account.
- Follow the setup process and make decisions on the security and compliance settings you want to implement.
-
- Integrating existing resources:
-
- Use AWS Organizations to create an organization that includes both the new Control Tower account and the existing account.
- Ensure AWS resource access is set up correctly between the accounts using AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM).
- Use AWS Resource Linking to link the desired resources in the existing account to the new Control Tower account.
-
- Testing:
-
- Validate that the resources are accessible in the new Control Tower account.
- Verify that the security and compliance policies set up in Control Tower are being applied to the integrated resources.
- Ensure that all business processes are working as expected in the new Control Tower account.
-
- Finalizing:
-
- Document the process, including any changes made to the resources during the integration process.
- Train any necessary staff on the new processes and policies set up in the new Control Tower account.
-
To access AWS resources from one account to another, you can use AWS Organizations or AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM).
- Using AWS Organizations:
-
- Create an AWS Organization that includes both accounts.
- Use AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) policies to control access to resources across accounts.
- You can delegate access to the other account by granting permissions in IAM policies.
-
- Using AWS Resource Access Manager (RAM):
-
- Create a resource share in the account that owns the resources.
- Authorize other accounts to access the shared resources.
- Use IAM policies to control access to the shared resources.
-
