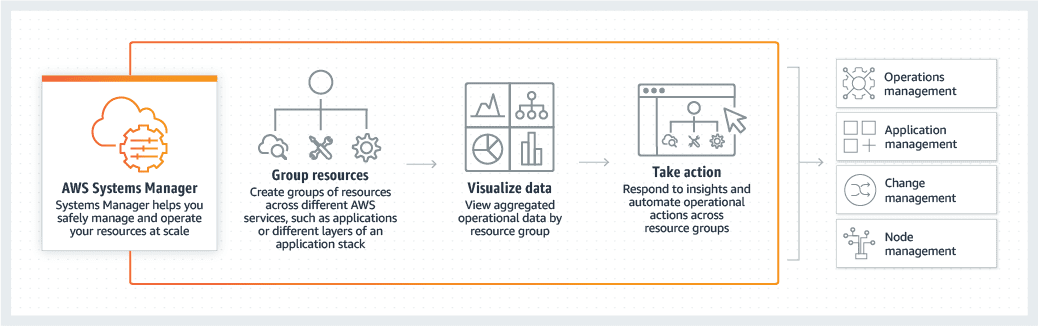
Fully Optimizing with Systems Manager
Management will need to continuously monitor and adapt AWS infrastructure to security and compliance requirements. Data will be aggregated to a single console from a variety of other insight services and third-party tools. Through automation, resource changes can be simplified whether they’re on-premises or in the cloud and issues can be diagnosed and remedied long before they impact end-users. There are a variety of features and AWS best practice methods that should be considered in how they are applied to an environment.
Using Automation
Patch Manager is a powerful tool within AWS Systems Manager that simplifies and automates common tasks, ensuring efficient maintenance and consistent execution. With Patch Manager, you can effortlessly generate backups, patch individual instances, deploy applications across multiple instances, and manage traffic control. One notable feature of Patch Manager is its ability to roll out security intelligence updates, guaranteeing that your systems remain protected against emerging threats.
To ensure utmost control and compliance, Patch Manager offers extensive configuration options. Using patch baselines, you can define rules that automatically approve or reject specific patches, such as operating systems or high-severity fixes. Moreover, you have the flexibility to override these rules by creating a list of patches that are automatically approved or refused based on your specific preferences. Patch Manager is an essential tool designed to streamline the maintenance and security of your instances. Here’s how it automates the process of keeping your software up-to-date and secure:
Automatic Scanning: Patch Manager periodically scans your managed instances to detect software missing crucial updates.
Patch Application: Once it identifies the missing patches, Patch Manager can apply these updates not just to a single instance, but simultaneously across multiple instances. This mass application is efficiently managed using EC2 instance tags, allowing for organized and targeted patching.
Security-Focused Baselines: For enhancing security, Patch Manager utilizes patch baselines. These baselines include sets of rules that automatically approve patches shortly after their release. This feature ensures that your systems are not left vulnerable for long after a new patch becomes available.
Patch Rules and Lists: Beyond automating approvals, these baselines also help you manage which patches are applied and which are not, with lists of approved and rejected patches. This level of customization helps maintain the integrity and security of your systems per your organizational policies.
CVE IDs Integration: Patch Manager supports CVE IDs, which are critical in identifying security vulnerabilities. By integrating CVE IDs, Patch Manager not only patches but also assists in proactively identifying potential security threats, aiding in quicker responsiveness to such risks.
Pre and Post-Patching Actions: You can configure Patch Manager to execute specific actions before and after patching. This capability is crucial for ensuring that the systems are prepared for the patch and are returned to normal operation without disruptions after the patching.
The Parameter Store and State Manager
AWS Systems Manager Parameter Store is a central repository for configuration data, ideally database connection strings, API keys, and other important information critical to the security of cloud infrastructure. Along with managing configuration data securely, it also provides secure access from multiple instances. This works well in conjunction with the State Manager. The state manager Continuously monitors and verifies that instances under the System Manager’s controls are configured correctly and adjusts settings if needed. Everything from security settings to network settings and individual application settings are tracked in the instance configuration.
The Principle of Least Privilege
Setting IAM (Identity Access Management) policies to follow the principle of least privilege means that each user role will only have access to the resources that are necessary to complete their tasks. Should an account become compromised, the amount of damage the hijacked account can do will be significantly reduced and minimize the risk of unauthorized access to crucial resources. Access logs will track suspicious activity to better discover which accounts in an AWS organization have been compromised.
Stick to a Good Naming Convention
Using a standardized method of naming resources will make those resources much easier to find and identify. The AWS Systems Manager does come with a tagging system to help categorize everything. This also works with properly allocating costs and properly tracking what services are using environmental resources for accounting and cost optimization purposes. Items with similar tags can then be placed into Resource Groups. These are groups of similar resource types, so sourcing the right resources is much easier.
Resource Groups are fundamentally used to organize and manage a collection of related AWS resources within a single AWS region. These groups are created based on specific criteria defined in a user query, ensuring that only resources meeting those criteria are included.
Managed Instances
Managed Instances are instances specifically located outside of an environment’s VPC running in another environment or in a customer’s data center. Typically, this is more for front-end requirements where customers will need access to certain resources and can help simplify how instances are managed across environments.
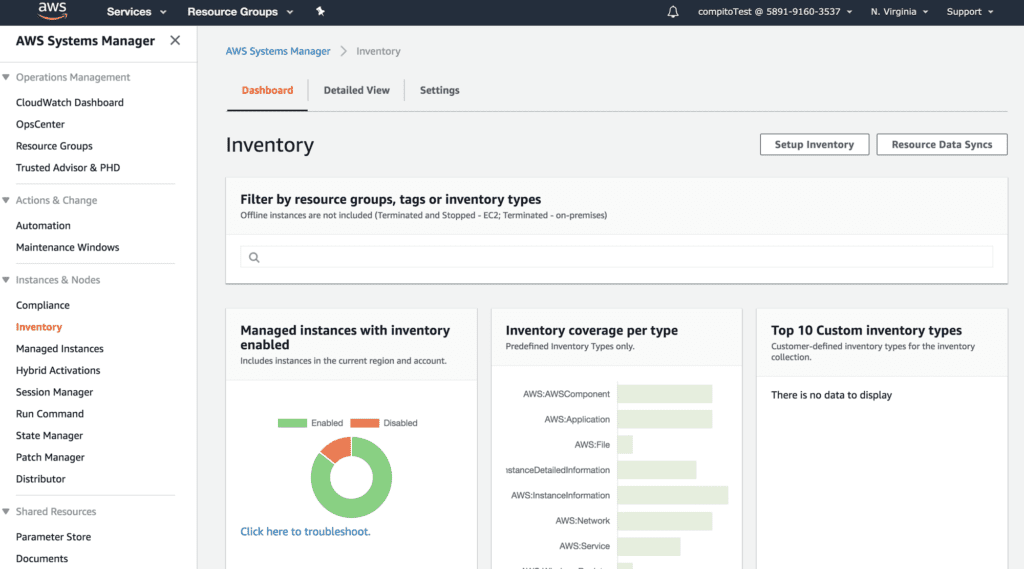
Inventory Management and Resource Use
The metadata on all active instances and applications is retained in the environment’s inventory. Everything from resource use and access logs is kept here with extensive details for review. These should be used extensively for evaluating environmental efficiency and identifying potential security issues that need to be remedied.
AWS Infrastructure and Maintaining Control
Systems Manager is a very comprehensive set of tools that grants significant oversight over an environment and the options for how to change the environment to be efficient, meet best practices, and mitigate risk as much as physically possible. Whether for development teams building their first project on AWS or companies who are long-time users of the Amazon Cloud, it’s an essential service that should be considered in the maintenance process. For more on AWS best practices, check out our guide on objectives and services that can help provide a sustainable AWS environment.
What is Configuration Compliance?
AWS Systems Manager offers several key features that enable efficient and secure infrastructure management. One of these features is Configuration Compliance. This ensures that your managed instances’ settings and configurations align with the desired state. This includes verifying both patch compliance and configuration consistency across your AWS accounts and Regions. Distributor is another valuable feature that provides a secure solution for storing and distributing software packages throughout your organization. It seamlessly works with other Systems Manager tools like Run Command and State Manager, giving you control over the lifespan of these packages on your instances. It also allows for viewing compliance history and change tracking for Patch Manager patching data and State Manager associations, all through the integration with AWS Config. Users can customize Systems Manager Compliance to create compliance types, tailoring them to meet specific organizational needs.
Distributor provides a secure solution for storing and distributing software packages throughout your organization. It seamlessly works with other Systems Manager tools like Run Command and State Manager, giving you control over the lifespan of these packages on your instances.
AWS Systems Manager provides comprehensive capability for storing various data types. It lets you securely store configuration data, such as database connection strings and plain-text values. Additionally, it offers the ability to store crucial secrets, like passwords and sensitive information, ensuring their protection and accessibility in a centralized repository.
AWS Systems Manager acts as a centralized repository for storing all configuration data, including sensitive information, in plaintext, keeping code segregated from secrets and configuration data. This design helps maintain your infrastructure’s security while allowing easy access to necessary data.
What is Distributor?
Distributor is a feature in AWS Systems Manager that provides a secure solution for storing and distributing software packages throughout your organization. It offers control over the lifespan of these packages on your instances by working seamlessly with other Systems Manager tools such as Run Command and State Manager. With Distributor, you can efficiently manage software distribution and ensure that the right packages are available on the right instances at the right time.
What types of data can be stored in AWS Systems Manager?
AWS Systems Manager provides a comprehensive solution for storing various types of data, encompassing both plain-text information and sensitive credentials. This includes the capability to securely store configuration data, such as database connection strings and other plain-text values. Additionally, AWS Systems Manager allows for the storage of crucial secrets, such as passwords and other sensitive information, ensuring their protection and accessibility in a centralized repository.
How does AWS Systems Manager help segregate code from secrets and configuration data?
AWS Systems Manager provides a comprehensive solution for storing various types of data, encompassing both plain-text information and sensitive credentials. This includes the capability to securely store configuration data, such as database connection strings and other plain-text values. Additionally, AWS Systems Manager allows for the storage of crucial secrets, such as passwords and other sensitive information, ensuring their protection and accessibility in a centralized repository.
How does AWS Systems Manager help segregate code from secrets and configuration data?
AWS Systems Manager is designed to assist in segregating code from secrets and configuration data in a secure manner. It serves as a centralized repository for storing all configuration data, including sensitive information such as passwords and database strings, in a plaintext format. By separating code from secrets and configuration data, it provides enhanced security and control over access to these valuable resources.
Parameters in AWS Systems Manager can be conveniently labeled and organized into hierarchies, making it easier to manage and handle them. This hierarchical structure allows for logical grouping of parameters based on their respective purposes or environments, such as development, production, or testing.
For example, the same parameter name, such as “?db-string,” can be used, but with different hierarchical paths like “?dev/db-string” or “?prod/db-string” to differentiate the values based on the specific environment they belong to. This practice helps maintain separation and avoids potential confusion between different instances of a parameter.
Moreover, AWS Systems Manager seamlessly integrates with AWS Key Management Service (KMS), which enables automatic encryption of the data stored within the system. This integration ensures that sensitive information, such as passwords and secrets, are protected, even if they are stored in plaintext format within the repository.
By leveraging AWS Systems Manager, organizations can effectively enforce a separation between code and sensitive information, maintaining a higher level of security and control over their configuration data.
What is the benefit of linking AWS Key Management Service (KMS) with Systems Manager?
Linking AWS Key Management Service (KMS) with Systems Manager offers the valuable advantage of automating data encryption. By integrating these two services, you can ensure that the data you store on AWS is automatically encrypted. With KMS, you have the ability to manage and control the encryption keys, while Systems Manager provides a centralized location for managing, configuring, and operating your AWS resources. This combination empowers you to enhance security by seamlessly encrypting your sensitive data within the AWS environment without the need for manual intervention.
How can AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) be used with parameters in Systems Manager?
AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) offers a solution for managing user and resource access to parameters in AWS Systems Manager. By utilizing IAM, you can efficiently control who has the permission to access parameters within the Systems Manager. IAM allows you to define fine-grained access policies, granting or revoking access based on specific user roles, groups, or individual users.
In addition to controlling user access, IAM also provides the ability to manage resource-level permissions. This means you can set restrictions on which resources, such as Amazon Elastic Container Service, AWS Lambda, and AWS CloudFormation, can reference the parameters. By configuring IAM policies appropriately, you can ensure that only authorized resources are able to access and utilize the parameters within Systems Manager.
Overall, leveraging AWS IAM in conjunction with parameters in Systems Manager provides a robust and secure approach to managing user and resource access, enabling you to have granular control and a higher level of security in your AWS environment.
