What is the Rule of 40?
The Rule of 40 states a software company’s combined revenue rate and profit margin must be at or above 40%. Above this level, SaaS companies are at a sustainable growth rate. By comparison, companies that are below this level may be experiencing cash flow or liquidity troubles. The Rule of 40 is a dependable standard to hold SaaS companies to because the SaaS sector maintains high margins between 70% and 90%. This makes comparison, regardless of business cycle and operating structure, generally easier to conduct.
As an advanced AWS partner, we bring unparalleled expertise to architect, deploy, and optimize cloud solutions tailored to your unique needs.
Rule of 40 Formula
The calculations discussed are all a part of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and should be consistent from company to company on how they are calculated after certain time periods. All of these values should be easy to derive from the most recent yearly income statements a company has. The formula is pretty simple and is defined as:
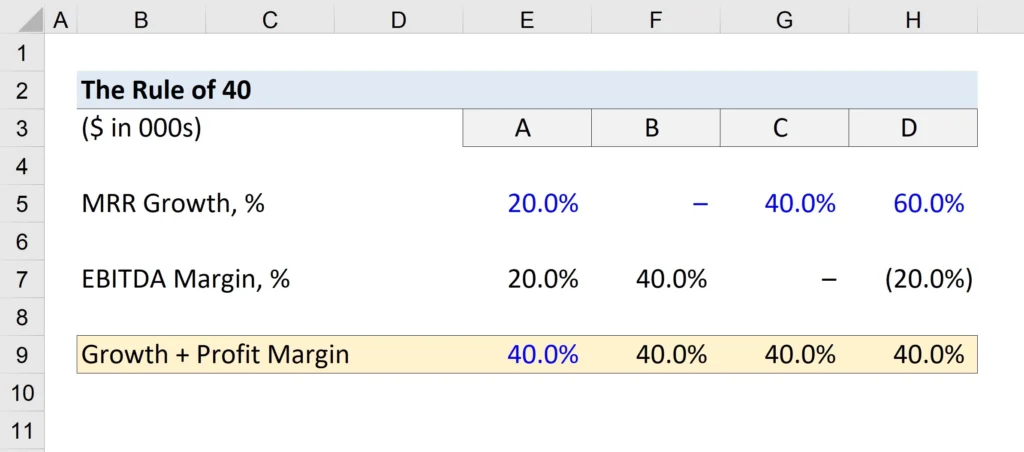
SaaS’ Growth Rate + the SaaS’ Profit Margin > 40%
There can be some troubles depending on whether the company measures its revenue growth using monthly or annual recurring revenue. The profit margin is commonly calculated using the margin of Earnings Before Interest, Tax, Depreciation, and Amortization (EBITDA) of a given period.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) = Total Number of Active Accounts * Average Revenue per Account (ARPA)
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) = MRR * 12 months
Growth Rate = (Current Year Value - Last Year Value) / Prior Year Value
EBITDA Margin (%) = EBITDA / revenue
Despite all these provided values, there is still some room for debate regarding what stage the rule should be applied to and its general reliability as a metric for SaaS companies. However, this threshold is simple enough to calculate and accurate enough to find popularity.
Why Do SaaS Companies use the Rule of 40?
Establishing How Much Breathing Room a SaaS Company Has
Establishing The Company’s Ability to Invest
Showing Investors the Potential SaaS Opportunities
Determining a SaaS Company’s Greatest Potential
Striking a Balance
Get Started Today!
At AllCode, our mission is to leverage our unique skillset and expertise to deliver innovative, top-tier software solutions that empower businesses to thrive in our world’s rapidly-evolving technological landscape.
Work with an expert. Work with AllCode