Microservice Architecture vs. Monolithic Architecture
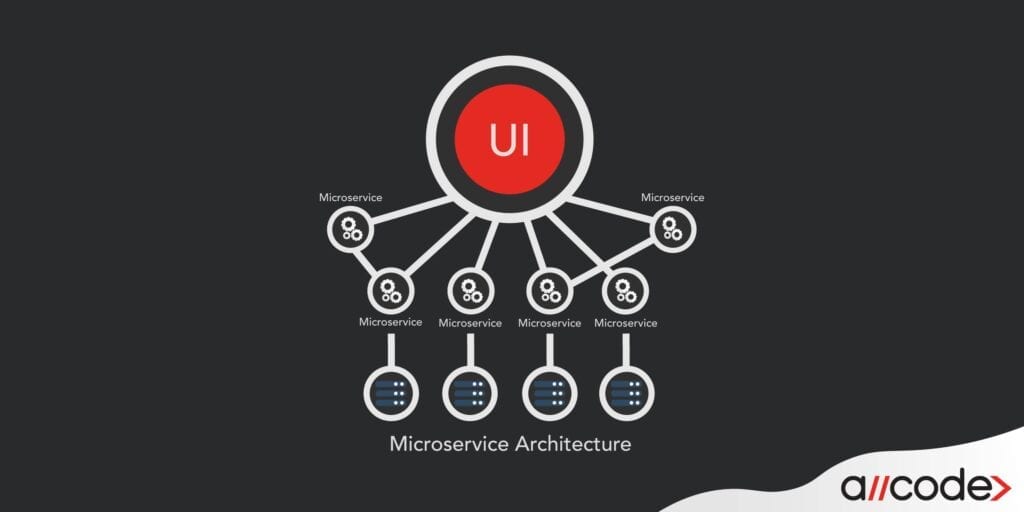
A microservice architecture is a critical way of keeping up with the technology curve of today’s ever-shifting digital world.
Over the past few years, microservices have become a popular option when developing web and mobile cloud applications. Tech giants like Amazon, Google, and Netflix have successfully used microservices in their organization to streamline their processes.
Many companies consider the microservice approach to be the most efficient method for business growth.
What is a Microservice Architecture?
Microservices are the state-of-the-art software development technique that structures the backend of an application into loosely coupled services that can be reused by other applications. Each service is self-contained and will implement a single business capability.
Mobile and cloud applications typically start with two repositories in source control. One repository makes use of the front-end and another repository for the backend.
By splitting your application into two repositories, you enable two different sets of engineers to work on the UI and backend simultaneously.
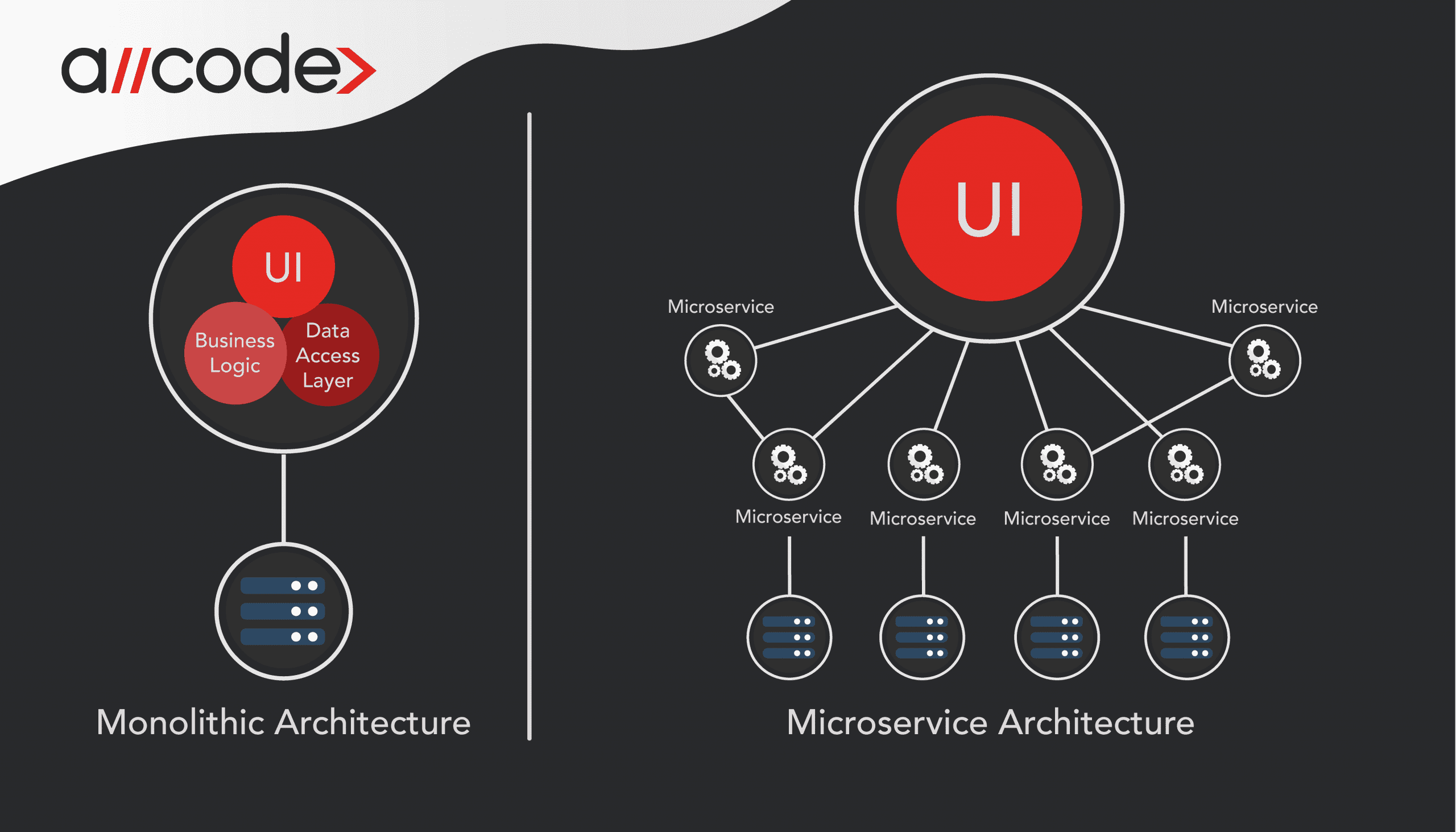
Drawbacks to a Monolithic Backend
Unfortunately, there are a few significant drawbacks to having a monolithic backend that consists of your business logic and data access layer:
- The sole responsibility of the backend is to serve data to the front end.
- The components within the monolithic backend are interconnected and interdependent.
- For developers to make changes to the backend, they have to build and deploy the entire stack at once.
- If the developers want to address scalability issues, the entire system must scale together.
- In the case that the developers want to adopt a new technology stack, you may have to rewrite the entire solution.
Benefits of a Microservice Architecture
By splitting your monolithic backend into business-specific services, you can address a number of the shortcomings of the monolithic backend.
A prime example of a self-contained microservice is authentication. Every application requires the user to signup, sign in, reset the password, perform email validation, etc.
An Authentication microservice allows you to solve many of the issues faced with the monolithic backend:
- Multiple applications can make use of the authentication microservice.
- The authentication microservice can make use of a REST API.
- Devs can make changes without modifying the rest of the application.
- The application outside of the authentication doesn’t have to change.
- To adopt a new technology stack for the authentication microservice, you only have to rewrite the single authentication service.
Conclusion
In subsequent blog posts, we will explore the various types of microservices that exist in a cloud SaaS application.
Learn how Allcode can help you!
Get in touch!
