Billing for Small Businesses
One of AWS’ biggest strengths is that its services and capabilities can tolerate different industries, sizes of companies, and levels of traffic intensity. New resources can be brought online and offline within seconds to minutes. However, the complex billing model can add an unnerving challenge to AWS for small businesses. Fortunately, AWS can provide ways that can help bring the average AWS cost for small businesses down.
Billing for Small Businesses
One of AWS’ biggest strengths is that its services and capabilities can tolerate different industries, sizes of companies, and levels of traffic intensity. New resources can be brought online and offline within seconds to minutes. However, the complex billing model can add an unnerving challenge to AWS for small businesses. Fortunately, AWS can provide ways that can help bring the average AWS cost for small businesses down.
The AWS Free Tier
While not all services incorporate the Free Tier, many do allow for a brief duration when AWS resources can be used at no cost. Depending on what the developers need, this allows them to either operate at a low scale at cheaper costs or to try out certain services without needing to unnecessarily rake up additional funds. Free Tier services can either be free for the first month or months after initiating them, free for the first whole year after signup, and/or free indefinitely within certain resource limitations. It’s a very welcome feature and we do cover it in greater detail in our own article.
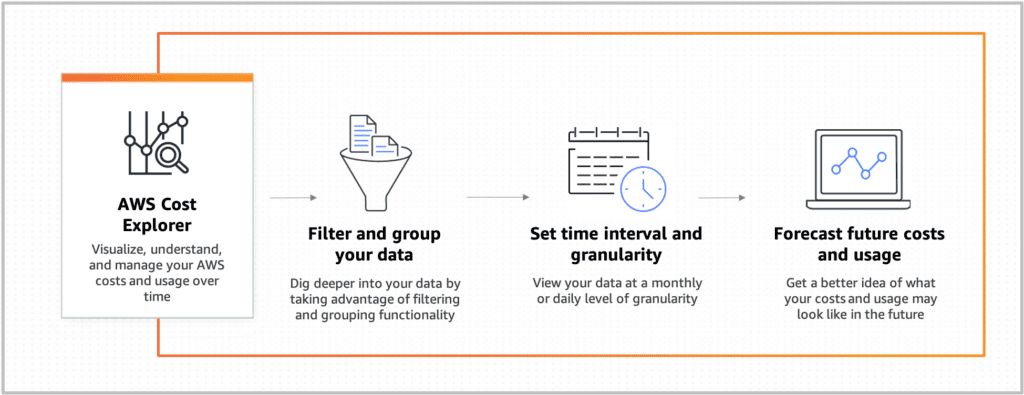
AWS Cost Explorer
At the absurdly low rate of $0.01 per request, Cost Explorer helps to tinker with and explore AWS model possibilities and what sort of monthly bill an account can expect. With an easy-to-understand visual UI, customers can tinker with what services they want to use and fully understand how each service contributes to the bill.
The AWS Free Tier
While not all services incorporate the Free Tier, many do allow for a brief duration when AWS resources can be used at no cost. Depending on what the developers need, this allows them to either operate at a low scale at cheaper costs or to try out certain services without needing to unnecessarily rake up additional funds. Free Tier services can either be free for the first month or months after initiating them, free for the first whole year after signup, and/or free indefinitely within certain resource limitations. It’s a very welcome feature and we do cover it in greater detail in our own article.
AWS Cost Explorer
At the absurdly low rate of $0.01 per request, Cost Explorer helps to tinker with and explore AWS model possibilities and what sort of monthly bill an account can expect. With an easy-to-understand visual UI, customers can tinker with what services they want to use and fully understand how each service contributes to the bill.
Choosing the Right Instance Type
Many services have different permutations they can combine computing power with, including compute resources, memory, and storage capacity. A big setback for many cloud services is the potential for over-provisioning resources the account does not need. Being more careful when choosing the initial instance can help avoid this.
Auto-scaling
Speaking of over-provisioning, AWS can scale depending on predicted traffic. Depending on the number of users for an application, new instances can be powered on to avoid demand being too taxing on existing instances. When traffic starts to slow down again, those extra instances will power down in turn.
Storage Options
It would be wise to consider what items are to be stored in the cloud and how they should be stored. Many of the storage services are tailored to either specific data types or to specific needs and solution types such as Simple Storage Service (S3) or Elastic Block Service (EBS). For longer-term and cost-effective storage options, AWS has Glacier with slower data transfer times, but less energy draw overall.
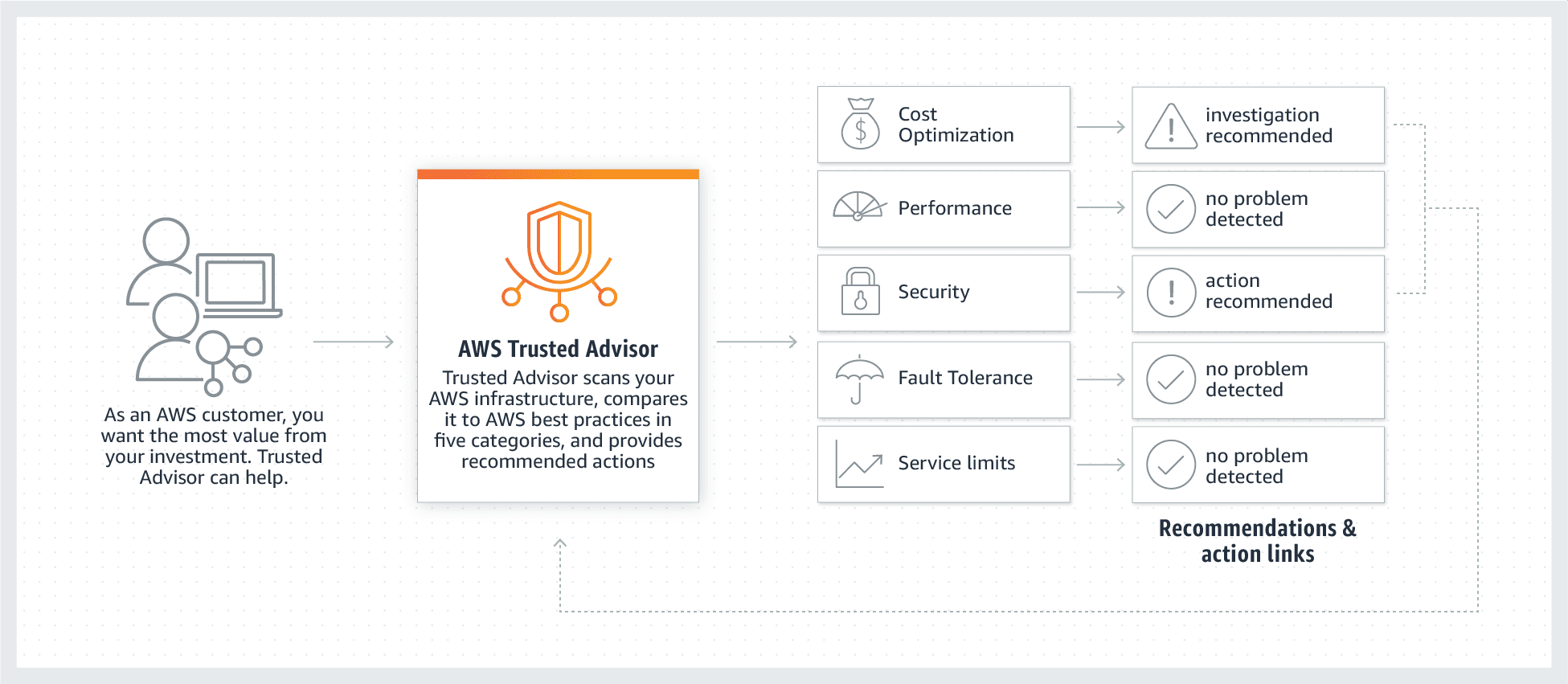
AWS Trusted Advisor
While it will require a subscription or a percentage of monthly AWS fees, Trusted Advisor evaluates an environment based on a checklist and verifies that it abides by best practices and is optimized as much as it can for cost. Points of use that do need optimization will be highlighted. For more information on subscription rates and other questions, check out the AWS page here.
Choosing the Right Instance Type
Many services have different permutations they can combine computing power with, including compute resources, memory, and storage capacity. A big setback for many cloud services is the potential for over-provisioning resources the account does not need. Being more careful when choosing the initial instance can help avoid this.
Auto-scaling
Speaking of over-provisioning, AWS can scale depending on predicted traffic. Depending on the number of users for an application, new instances can be powered on to avoid demand being too taxing on existing instances. When traffic starts to slow down again, those extra instances will power down in turn.
Storage Options
It would be wise to consider what items are to be stored in the cloud and how they should be stored. Many of the storage services are tailored to either specific data types or to specific needs and solution types such as Simple Storage Service (S3) or Elastic Block Service (EBS). For longer-term and cost-effective storage options, AWS has Glacier with slower data transfer times, but less energy draw overall.
AWS Trusted Advisor
While it will require a subscription or a percentage of monthly AWS fees, Trusted Advisor evaluates an environment based on a checklist and verifies that it abides by best practices and is optimized as much as it can for cost. Points of use that do need optimization will be highlighted. For more information on subscription rates and other questions, check out the AWS page here.
Usage Monitoring
AWS CloudWatch can help keep an eye on everything that happens within an environment and provide windows of opportunity for cost saving, such as unused or underutilized resources that would benefit from auto-scaling functionality. Alternatively, it keeps a log of all changes made within the environment and can be used for either rolling back issues or inspecting security breaches.
Reserved Instances
Some instances could be critical for operation, but not require use year round. If an instance will likely be needed in the future but not currently, users have the option to reserve an instance for up to one or three years at a heavily discounted hourly rate. This will prevent other accounts from occupying those instances when they are needed to increase operational capacity. Alternatively, if the account holders no longer need an instance whereas another account does, the instance owner can sell the instance instead.
Spot Instances
These instances see much lower demand and use in the AWS cloud. As such, they get much lower rates compared to other AWS instances. These instances still retain the stability and resilience of normal instances, but are capable of handling operations at scale and can have their operations interrupted at any time. Ideally, these spot instances are much better for handling non-critical workloads while simultaneously minimizing the cost of handling those workloads.
Slow Adoption
AWS is a very complex platform with an absurdly steep learning curve, especially with a lack of proper technical expertise. Having a certified expert can help not only lower costs, but understand and establish more technical requirements, such as best practices and security. If you are a small company looking to improve business operations using the cloud, at the very least drop us a line for some advice
Usage Monitoring
AWS CloudWatch can help keep an eye on everything that happens within an environment and provide windows of opportunity for cost saving, such as unused or underutilized resources that would benefit from auto-scaling functionality. Alternatively, it keeps a log of all changes made within the environment and can be used for either rolling back issues or inspecting security breaches.
Reserved Instances
Some instances could be critical for operation, but not require use year round. If an instance will likely be needed in the future but not currently, users have the option to reserve an instance for up to one or three years at a heavily discounted hourly rate. This will prevent other accounts from occupying those instances when they are needed to increase operational capacity. Alternatively, if the account holders no longer need an instance whereas another account does, the instance owner can sell the instance instead.
Spot Instances
These instances see much lower demand and use in the AWS cloud. As such, they get much lower rates compared to other AWS instances. These instances still retain the stability and resilience of normal instances, but are capable of handling operations at scale and can have their operations interrupted at any time. Ideally, these spot instances are much better for handling non-critical workloads while simultaneously minimizing the cost of handling those workloads.
Slow Adoption
AWS is a very complex platform with an absurdly steep learning curve, especially with a lack of proper technical expertise. Having a certified expert can help not only lower costs, but understand and establish more technical requirements, such as best practices and security. If you are a small company looking to improve business operations using the cloud, at the very least drop us a line for some advice
