What is AWS?
Before the advent of cloud computing, the world faced several challenges in terms of scalability, redundancy, and server provisioning. In order to establish any sort of digital infrastructure, organizations had to invest in their own hardware, servers, and data centers, while also hiring staff to manage the entire setup. This exclusive approach meant that startups and financially constrained businesses found it exceptionally difficult to secure the necessary capital upfront to launch their first website or build a database. The absence of cloud computing created a barrier for entry into the digital realm, hindering innovation and growth for smaller entities. Additionally, organizations had to cope with the risk of overprovisioning, where they invested heavily in resources to accommodate unexpected spikes in capacity. These challenges in scalability, redundancy, and cost management limited the accessibility and feasibility of establishing a strong digital presence for many businesses.
AWS offers businesses a comprehensive suite of integrated services designed to optimize various aspects of their operations. With a market-leading 32.4% share, Amazon is the go-to cloud provider trusted by countless organizations worldwide. The beauty of AWS lies in its pay-as-you-go model, allowing businesses to scale their usage according to their needs. The less you use, the less you pay, and the more you use, the less you pay per unit.
However, AWS goes beyond mere cost-effectiveness. It was born out of Amazon’s need to expand its internal IT infrastructure, but it has since grown into a multi-billion-dollar company. Today, AWS not only supports Amazon’s IT backbone but also empowers industry titans like Netflix, Dropbox, and Reddit, among others. This level of trust and widespread adoption speaks volumes about AWS’s reliability and capabilities.
AWS operates as an “Operating System of the Internet,” treating different hardware resources as isolated components within this ecosystem. These resources are then transformed into managed services, removing the burden of managing hardware and physical infrastructure from developers’ shoulders. This revolutionary approach eliminates the need for businesses to invest precious time and resources in maintaining their infrastructure and instead allows them to focus on their core value proposition.
AWS provides several key advantages for businesses looking to optimize their IT infrastructure:
Flexibility and Scalability: AWS allows organizations to adapt their resource usage based on current needs, ensuring they can scale up or down effortlessly without incurring unnecessary costs. This flexibility means companies pay only for the resources they consume, offering a cost-effective solution compared to maintaining on-premises systems.
High Reliability and Availability: AWS leverages Amazon’s vast global network infrastructure, including many servers spread across numerous data centers worldwide. This setup ensures high levels of availability and redundancy, safeguarding against data center failures and ensuring continuous access to applications and data.
Comprehensive Service Offering: AWS provides a broad spectrum of services geared towards various IT needs. From computing power and storage solutions to database management, content delivery, and advanced analytics including machine learning capabilities, AWS empowers businesses to develop a wide range of applications and solutions tailored to their specific requirements.
AWS Learning Opportunities
Amazon offers training courses and events designed to help individuals build and validate their skills so that they can maximize the full potential of the cloud. These courses are regularly adjusted with AWS updates so that users are leveraging the latest cloud skills.
Both digital and classroom learning opportunities are available depending on the user’s preference for various services for things like IoT and big data. With classroom training, AWS experts will teach the class and provide best practices, while virtual training allows you to learn from anywhere at your own pace.
Due to COVID-19, some in-person learning options may be limited or changed to virtual sessions.
APN Partner Training
The Amazon Partner Network (APN) is a global program designed for technology and consulting AWS experts to build solutions for customers. The APN offers proprietary tools and support that help companies grow, market, and sell their AWS offerings.
Partners can deepen their learning and capabilities through training courses. These courses give partners the chance to become AWS certified as a cloud practitioner, architect, developer, and operations.
Enterprise Training
AWS offers courses geared towards helping enterprises achieve business goals by building cloud fluency across their organization. These learning resources can help companies create a culture of innovation and modernize current processes.
Learning Paths by Solutions or Roles
Whether you’re interested in training for a particular role or want to grasp different solutions, Amazon offers learning paths to help you.
Role learning paths:
• Cloud Practitioner
• Architect
• Developer
• Operations
Solution learning paths:
• Databases
• Machine Learning
• Media Services
• Storage
Pop-up Lofts
Amazon has “pop-up lofts” in San Francisco, New York, Berlin, Tel Aviv, and London used as workspaces and to learn about AWS opportunities. Due to COVID-19, these locations are indefinitely closed.
Events and Webinars
Amazon hosts, both online and in-person, events to bring the cloud computing community together. These events are designed for enthusiasts to collaborate, connect, and learn about the potential of AWS.
AWS Facts
- AWS has deployed 5 times more cloud infrastructure than competitors combined.
- 190 countries AWS has customers in.
- 8,000+ partner network members.
- 1,900+ third-party products.
Companies using AWS
Companies of all sizes use AWS services in some shape or form. According to Intricately, Amazon has 1,240,804 users utilizing their products and services as of July 6th, 2020.
A few of the big monthly spenders include:
1. Netflix - $19 Million
2. Twitch - $15 Million
3. LinkedIn - $13 Million
4. Facebook - $11 Million
5. Turner Broadcasting - $10 Million
6. BBC - $9 Million
7. Baidu - $9 Million
8. ESPN - $8 Million
9. Adobe - $8 Million
10. Twitter - $7 Million
History of AWS
Cloud computing has revolutionized the world of computing and IT, bringing about significant changes and advancements. Before the advent of cloud technology, businesses faced numerous challenges in terms of scalability, redundancy, and server provisioning. To establish a digital presence, companies had to invest heavily in purchasing their own hardware, servers, data centers, and hiring staff to manage them. This posed a significant barrier, particularly for start-ups and cash-strapped businesses, as they struggled to gather enough capital to launch websites or build databases.
Companies now can trade capital expenses for variable expenses, eliminating the need for upfront investments in expensive hardware and infrastructure. This shift towards variable expenses has empowered businesses of all sizes, allowing them to allocate financial resources more efficiently and effectively. By leveraging cloud infrastructure, companies can benefit from massive economies of scale, as cloud providers can optimize their resources to serve multiple clients simultaneously.
Cloud computing also enhances speed and agility in IT operations. With on-demand resource access, businesses can quickly deploy and provision servers, launch new applications or websites, and respond rapidly to changing market demands. This increased agility enables companies to bring products and services to market faster, providing a competitive edge in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
Furthermore, the cloud allows businesses to focus on what truly matters - their core competencies and objectives. By offloading infrastructure management and maintenance to cloud providers, companies can free up valuable time and resources that can be redirected towards innovation, developing new features, and improving customer experiences. This shift enables companies to concentrate on strategic initiatives that drive their growth and success.
Amazon was the first company to market cloud infrastructure services when it launched Amazon EC2 in 2006. They monopolized this service until competitors like Microsoft and Google responded with their cloud infrastructure services in 2008.
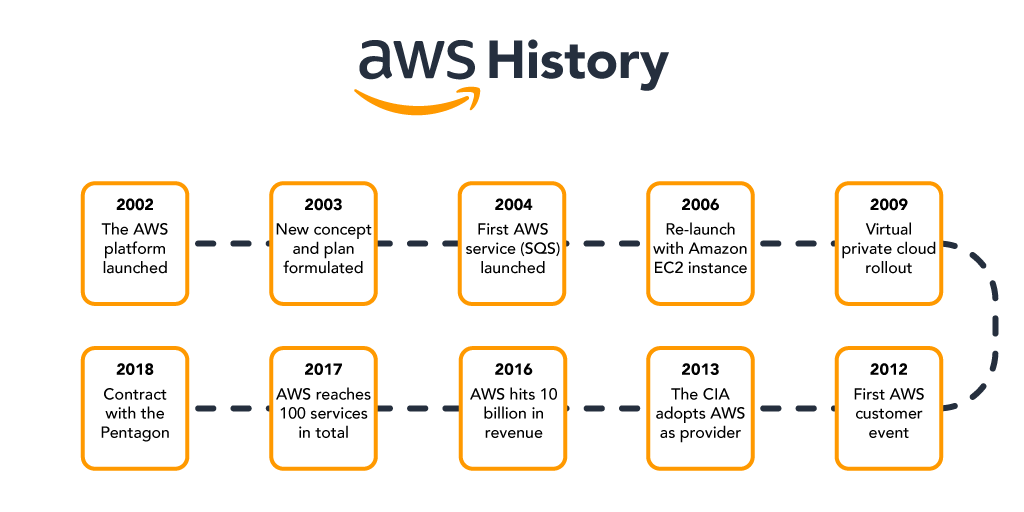
2002 - The platform was launched
2003 - Concept was reformulated with standardized plans
2004 - The first service (Simple Queue Service) launched for public usage
2006 - Official re-launch with Amazon EC2
2009 - Virtual Private Cloud launches
2012 - Holds first customer event
2013 - CIA adoption
2016 - Reaches 10 billion in revenue target
2017 - 100 services in total
2018 - Signs 10 billion dollar contract with the Pentagon
Future Possibilities
The future is looking remarkably bright for AWS – with an annual growth of circa 40%, there is no sign of the cloud going anywhere, and it is important to realize where this world has come from. AWS’s ability to consistently evolve and provide scalable solutions ensures that it will continue to dominate the cloud market. This robust growth projection highlights the increasing reliance on cloud services and underscores AWS’s pivotal role in shaping the future of digital landscapes. As businesses continue to transition to cloud-based operations, AWS is poised to meet their evolving needs, driving innovation and transformation across industries.
Did we miss something?
Why Amazon Lambda?
Lambda offers a multitude of benefits, making it an ideal choice for your computing needs. By simply uploading your code as a ZIP file or container image, Lambda effortlessly locates the required computing power and executes it based on incoming traffic. This seamless process allows you to focus on your application’s functionality without worrying about infrastructure management.
One of the key advantages of Lambda is its ability to work harmoniously with other AWS services through a few simple calls from your application. This integration saves you time and effort, as Lambda is optimized to collaborate effortlessly with services such as S3, Cognito, and DynamoDB.
Another notable benefit of Lambda is the option to enable Provisioned Concurrency, allowing you to run your program back-to-back in a matter of milliseconds. This feature ensures that your application remains responsive and delivers consistent performance, even during periods of high demand.
By default, Lambda is capable of working with a wide selection of programming languages including Node.js, Java, and Python. For testing functionality and building, Lambda files can be developed on both serverless and container applications such as AWS SAM.
